The Evaluation of Integrated Perfusion - Weighted Imaging Diffusion and Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Methods Accuracy for Brain Neoplasms Diagnosis Compared to Pathology Findings
Main Article Content
Abstract
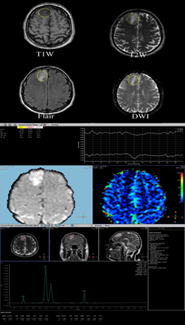
Background: MRI has a vital role in the assessment of brain neoplasm. Conventional MRI has limited specificity. The combination of MRI using diffusion-weighted imaging, perfusion-weighted imaging and magnetic resonance spectroscopy allows more accurate assessment of the tissue microenvironment. Objective: The role of diffusion-weighted Perfusion - Weighted Imaging, and Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy techniques to evaluate the Accuracy of Brain Neoplasms Diagnosis. Method: This project is based on cross-sectional design. The population of this study were 80 patients with brain tumors that have been indicated for MRI test in the period of sampling which was during February 2023 to July 2023. The data-collecting technique was done by the researcher using a questionnaire, observation, and laboratory findings. The questionnaire was designed and copied by the researcher. MRI examinations was performed using MRI 1.5 T scanner (Philips MULTIVA systems) using a phase array 6 channels head coil at the radiology department. The data had encoded and then entered into the statistical program (SSPS version 26). Results: A total 80 of six equally collected group samples were investigated radiographically for brain (8, 9, 17, 31, 7, and 8 patients) respectively after the inclusion and exclusion criteria. The age of each study sample was normally distributed and ranged from 10 to 86 years without significant differences between them (P-value= 0.16). One patient out of 80 was diagnosed incorrectly when using MRS sequence. Therefore, the achieved total accuracy, sensitivity and specificity are 97.61%, 100% and 87.5% respectively. The achieved p-value among study’s groups is 0.6. Although it is highly significant and accurate in the MRS procedure, additionally, the p-value when implementing the three independent sample ANOVA-test between the Choline, creatine and NAA is high significant with p value choline being 0.0001 and p-value for NAA being 0.0024 which means that there are highly significant differences between tissue brain groups. 80 patients were diagnosed correctly when using combining diffusion, perfusion and MRS sequence. Therefore, the achieved total accuracy, sensitivity and specificity are 100%, 100% and 98.9% respectively. Additionally, the achieved p-value of overall diagnosing result is 0.75 which confirms that no patients failed to diagnose by combining DWI, PWI and MRS than separate protocol. Conclusion: In this study we found that it is possible to diagnose brain malignancies with a greater level of sensitivity and accuracy by combining perfusion, diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI), and magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS). It has been found that using the CBF and CBV parameters for diagnosing brain lesions is more effective than using the MTT and TTP parameters. The NAA and Choline parameters are superior to the Creatinine parameter in terms of their ability to accurately diagnose brain lesions. The combination of DWI, MRS, and MRP predicted 100% sensitivity and Specificity 98.6% and accuracy 100% for the differentiation of the type of brain tumor. These cutting-edge MRI techniques eliminated the need for invasive treatments like transcranial biopsies.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.